In the era of accelerated digital transformation, the pain points of asset management such as "large quantity, diverse types, high value, and long service cycle" have become increasingly prominent. Traditional management models, plagued by low efficiency, poor real-time performance, and high error rates, seriously restrict enterprise development. As an innovative application of contactless automatic identification technology, the RFID Asset Management System has completely revolutionized asset control methods and become a core solution for enterprises to achieve intelligent and efficient asset management. This article will comprehensively analyze the key information of RFID asset management through five core questions, helping enterprises quickly implement effective asset control solutions.

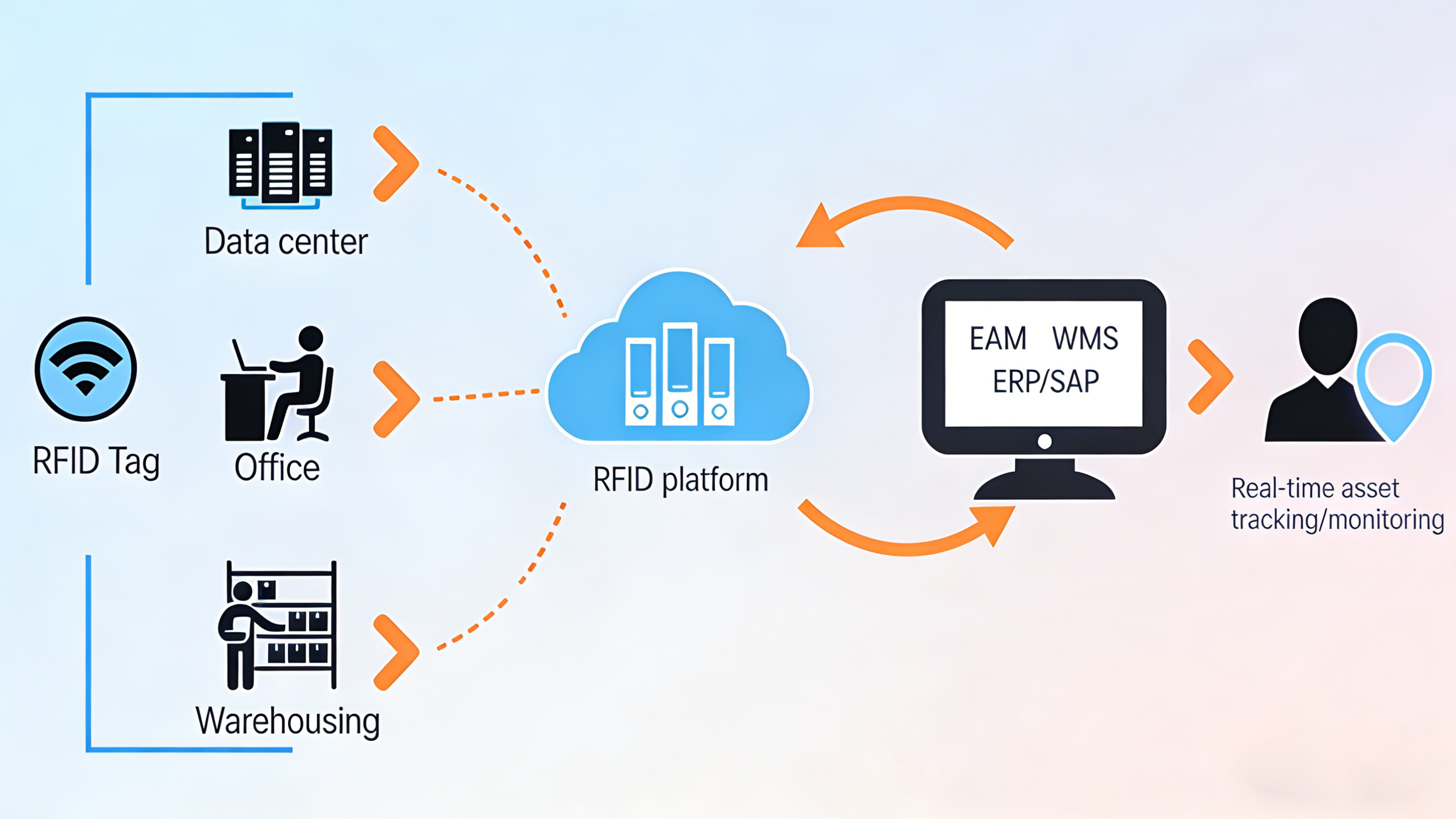
An RFID Asset Management System is a contactless automatic identification system based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, integrated with network technology and software technology. It automatically identifies target assets and collects relevant data through RF signals, realizing full-process management such as real-time monitoring, automatic recording, and intelligent inventory of assets. Its core value lies in breaking the limitations of traditional manual management, enabling assets to "speak for themselves" and transforming from passive statistics to active tracking.
1.Readers and Antennas: Interact with RFID tags through wireless communication to complete tag identification and data reading/writing, serving as the core terminal for signal transmission;
2.RFID Electronic Tags: Attached to the surface of assets, storing key information such as asset name, model, and barcode number to achieve unique asset identification (anti-metal tags are commonly used in IT asset management);
3.Card Issuers: Write basic data into tags, support password-locking of data areas to prevent information tampering;
4.Handheld Terminals: Quickly read asset tag information to realize mobile inventory and synchronize data to the background server in real time;
5.Management Software Platform: Includes a PC-side asset control platform and handheld software, responsible for data storage, analysis, report generation, and full-process business management.
The core of RFID asset tracking is a wireless data closed loop of "tag-reader-server", with the specific process as follows:
1.The RFID electronic tag attached to the asset stores a unique identifier and asset information;
2.The reader transmits RF signals through the antenna to cover the target area;
3.After receiving the signal, the tag is activated and feeds back the stored asset data to the reader;
4.The reader transmits the data to the background server, and the management software completes data storage, verification, and update;
5.Managers can real-time view asset status, location, circulation records, and other information through the software platform.
The entire process requires no manual contact, supports long-distance and batch identification, and completely solves the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive, and error-prone traditional manual inventory.
Compared with traditional barcode and manual management models, the core advantages of the RFID Asset Management System lie in full-process efficiency improvement and risk control, including:
• Long-distance and rapid identification: Supports batch reading, increasing inventory efficiency by 5-10 times without close contact with assets;
• High reliability and confidentiality: RF signals are resistant to pollution and interference, and tag data can be encrypted to prevent information leakage;
• Full-lifecycle management: Covers the entire process of asset procurement, registration, transfer, maintenance, and scrapping, dynamically updating asset status;
• Real-time visual control: Asset reports are clear and intuitive, supporting on-demand queries and solving the pain points of chaotic management and poor real-time performance;
• Flexible multi-mode inventory: Supports online/offline and single-person/collaborative inventory, adapting to different enterprise scenarios;
• Intelligent event reminders: Automatically alerts for asset expiration maintenance, abnormal movement, tag tampering, etc., with SMS notification support;
• Easy expansion and operation: The system can be upgraded according to enterprise scale, with a user-friendly interface that reduces personnel training costs;
• Unique identification and hierarchical management: Each asset corresponds to an exclusive electronic tag, facilitating classification, grading, and rapid positioning.
With high adaptability, the RFID Asset Management System has been widely applied in various industries to realize automated and intelligent asset control. Core application scenarios include:
• Factory equipment and fixed assets: Track production equipment and mechanical components to reduce idleness and maintenance costs;
• IT asset control: Full-lifecycle tracking of servers, computers, printers, and other IT equipment to prevent loss and abuse;
• Office and educational assets: Intelligent inventory and circulation management of office furniture, teaching instruments, books, and archives;
• Medical and elderly care assets: Real-time positioning and disinfection traceability of medical devices, rehabilitation equipment, and elderly care supplies;
• Special scenario management: Tamper-proof and loss-proof tracking of firearms, valuable instruments, trees, and electronic components.
• One-stop business management: One-click processing of daily asset operations such as addition, modification, transfer, borrowing, and depreciation calculation;
• Rapid asset inventory: Real-time collection of asset data, automatic generation of inventory reports, and traceable historical records;
• Batch efficient warehousing: Automatic scanning and entry by RFID equipment, with asset information synchronized to the background, improving warehousing efficiency by more than 3 times;
• Automatic abnormal alarms: Real-time alerts for asset loss, illegal movement, tag removal, etc., to stop losses in a timely manner;
• Data report analysis: Generate reports on asset circulation, usage efficiency, depreciation, etc., to support management decisions.
RFID tags are the core carrier of asset identification and should be selected based on asset material, usage environment, and management requirements. They are mainly divided into two categories: ordinary RFID tags and anti-metal RFID tags (ordinary tags are not suitable for metal surfaces, while anti-metal tags can be adapted to metal assets). Detailed descriptions of each tag type and a summary table are as follows:
Ordinary RFID Tag (for Library/Office Asset Management): This is the most common RFID electronic tag in fixed asset management. Compared with traditional barcode labels, it has advantages such as fast reading, short-distance scanning, and adjustable reading distance. It has a wide range of applications, being convenient and efficient. It is suitable for non-metallic assets such as wood, plastic, and paper, including desks, chairs, office furniture, and library books.

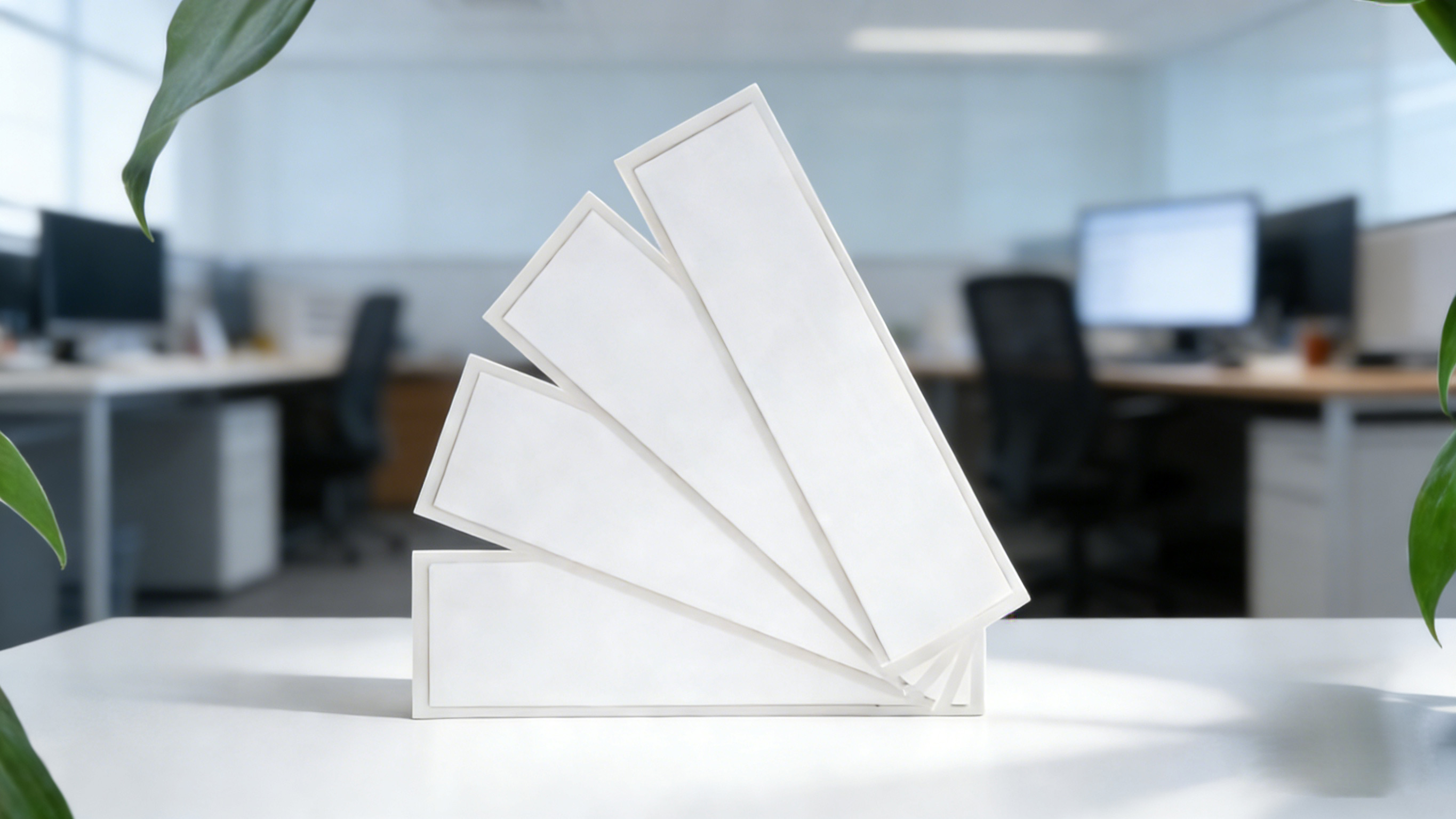
Soft Flexible Anti-Metal Tag (for Office Asset Management): Specially designed for objects with metal surfaces, this tag features a long reading distance, high sensitivity, small size, and easy installation. Its surface can print visual data, making it a cost-effective solution for indoor asset management such as computer asset management. It is mainly used indoors for IT assets and office equipment like computers and refrigerators.

ABS Anti-Metal Tag (for IT Asset Management): Made of high-temperature-resistant industrial ABS plastic with built-in metal shielding material, this hard tag works well on metal surfaces. It is corrosion-resistant and impact-resistant, suitable for outdoor use, and is widely applied in IT asset management, vehicle management, and outdoor electrical appliances.
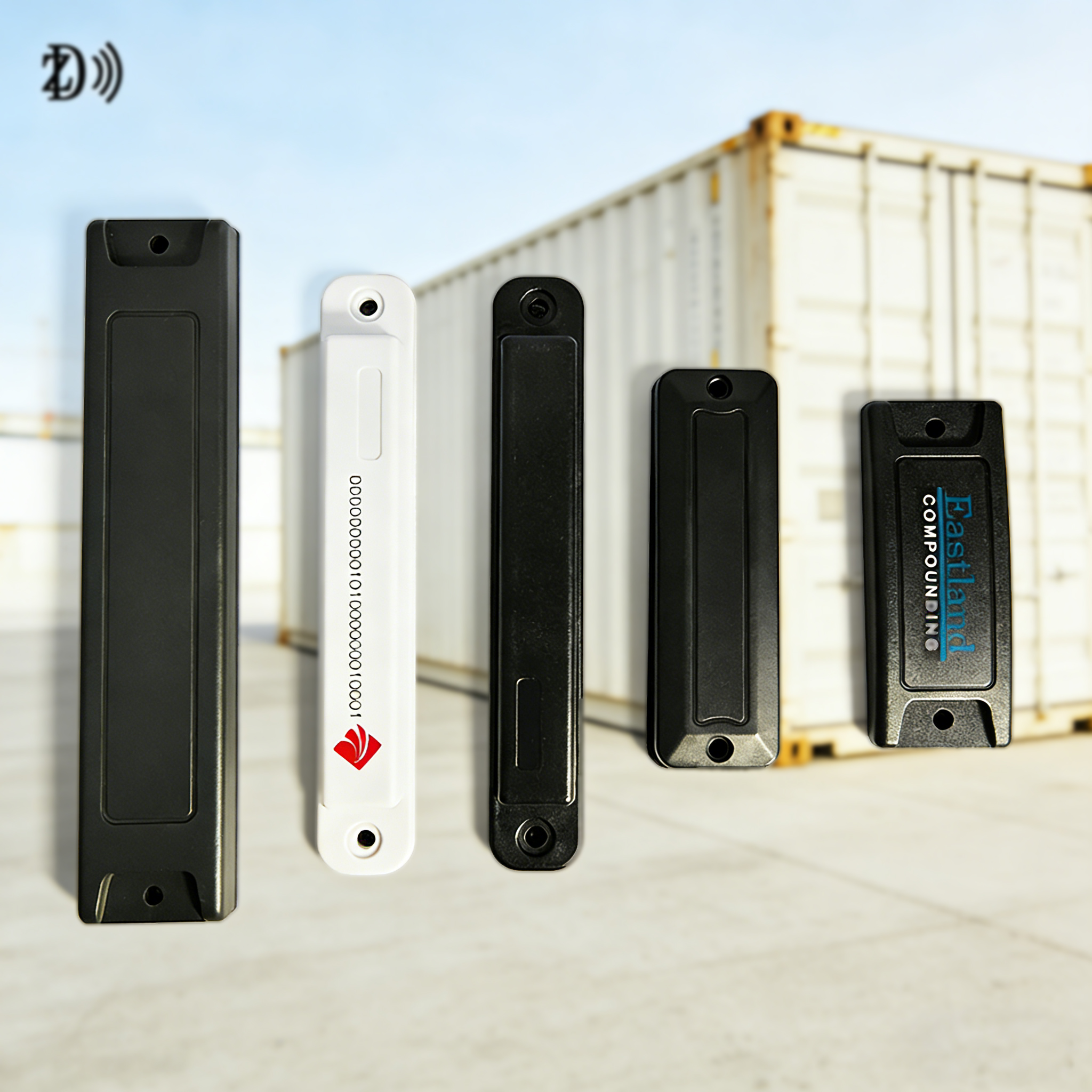

RFID PCB Tag (for Large Equipment Management): Packaged with PCB material, this tag has a specially designed internal circuit as the antenna. It performs excellently on metal objects, just as ordinary RFID tags do on wooden objects and cardboard boxes. Additionally, it offers advantages such as low cost and flexible design, making it an ideal solution for IT asset management, tool and equipment management.

RFID Ceramic Tag (for Electronic Components Management): An electronic tag packaged with ceramic material, it boasts high electrical characteristics, high performance, small size, fragility, and anti-transfer properties. The electronic tag antenna on the ceramic substrate has the advantages of low dielectric loss, good high-flatness characteristics, stable antenna performance, and high sensitivity. It is particularly suitable for asset management of electrical components and precision instruments.

RFID Tree Nail Tag (for Tree Management): Designed for timber asset management or tree tracking, this tag can be directly embedded into objects, making it difficult to destroy or remove. It is highly suitable for tree and wood tracking and identification. Available in various sizes and chip options to meet different application needs, it has an excellent reading distance thanks to its ferrite core antenna. It is widely used in tree management, park asset management, and furniture management.

Tag Type | Storage Capacity | Operating Temperature | Reading Distance | Typical Applications |
Ordinary RFID Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -20℃ ~ +85℃ | 5m | Desks, chairs, office furniture, library books, etc. |
Soft Flexible Anti-Metal Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -40℃ ~ +85℃ | 0.5-2 meters (related to reader, antenna size, and environment) | IT asset management, office assets (e.g., computers, refrigerators) |
ABS Anti-Metal Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -40℃ ~ +85℃ | 2-30cm (varies by reader and working environment) | IT asset management, vehicle management, outdoor appliances, etc. |
RFID PCB Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -40℃ ~ +180℃ | More than 1.5m | Tool asset management, large equipment management, etc. |
RFID Ceramic Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -40℃ ~ +220℃ | 1cm ~ 10m (varies by reader and working environment) | Electronic components management, precision instrument management, etc. |
RFID Tree Nail Tag | Depends on the selected RFID chip | -25℃ ~ 65℃ | 1cm ~ 10m (varies by reader and working environment) | Tree management, park asset management, furniture management, etc. |
1. Is the RFID Asset Management System expensive to implement?
The initial investment includes hardware (readers, tags, handheld terminals) and software customization, but the long-term return is significant. It reduces labor costs by 30-50% (e.g., inventory time cut from weeks to days), minimizes asset loss (by 20-40% on average), and improves asset utilization. For small and medium-sized enterprises, modular solutions are available to reduce upfront costs.
2. Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, most RFID tags (especially anti-metal tags like ABS, PCB, and flexible types) are reusable. The data can be rewritten via a card issuer, allowing the tag to be transferred to new assets after the original asset is scrapped. Ordinary paper-based RFID tags are usually disposable due to lower durability.
3. How is RFID different from traditional barcodes for asset management?
Barcodes require line-of-sight scanning, support only single-item reading, and are prone to wear and tear. RFID supports non-line-of-sight, long-distance, and batch reading (up to hundreds of tags at once), is resistant to pollution/wear, and can store more data (e.g., asset maintenance records). RFID is far more efficient for large-scale, high-value asset management.
4. What if my assets are mostly made of metal? Can RFID work?
Yes, but you must use anti-metal RFID tags. Ordinary tags are blocked by metal and cannot transmit signals. Anti-metal tags (flexible, ABS, PCB, ceramic) use special shielding materials to avoid signal interference, ensuring stable performance on metal surfaces. Choose flexible tags for indoor IT equipment and ABS/PCB tags for outdoor or heavy-duty metal assets.
5. Is the data stored in RFID tags secure?
Absolutely. The system supports data encryption for tags, and card issuers can set passwords to lock the data area—preventing unauthorized rewriting or tampering. Additionally, data transmitted between readers and the server is encrypted via network protocols, ensuring asset information is not leaked.
6. Can the RFID system integrate with my existing ERP/OA software?
Most professional RFID Asset Management Systems offer open APIs, enabling seamless integration with common ERP (e.g., SAP, Oracle), OA, or financial management software. This avoids data silos and ensures consistent asset information across all enterprise systems.
7. How long does it take to install and deploy the system?
The deployment time depends on the scale of assets. For small enterprises (hundreds of assets), it can be completed in 1-2 weeks (including tag affixation, data entry, and staff training). For large enterprises (tens of thousands of assets), deployment may take 1-3 months, but modular implementation allows phased launch (e.g., starting with IT assets or factory equipment).
8. What maintenance is required for the RFID system?
Routine maintenance is minimal:
• Tags: Check for damage (especially for outdoor assets) and replace if necessary (most tags have a service life of 5-10 years);
• Readers/handheld terminals: Regularly charge, clean, and update software;
• Software: Update to the latest version for new features and security patches.
Most vendors provide annual maintenance services to ensure system stability.
Through three core capabilities of "automatic identification, real-time tracking, and intelligent analysis", the RFID Asset Management System completely solves the pain points of "low efficiency, high error rate, and opacity" in traditional asset management. It realizes visual control of assets throughout their lifecycle from procurement to scrapping, helping enterprises reduce management costs, improve asset utilization, and avoid asset loss risks.
Whether it is factories, hospitals, schools, IT enterprises, or government agencies, all can achieve asset control upgrades through adapted RFID solutions. If you need to customize an RFID asset management solution based on your specific business scenario or obtain professional advice on tag selection, please feel free to contact us. We will help your enterprise quickly enter t he ranks of intelligent asset management!
Do you need a professional team to provide you with solutions? Contact us for a quote
Let us discuss it with you.